How to Draw Class Diagram in Visual Paradigm
The UML Class diagram is a graphical notation used to construct and visualize object oriented systems. A class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static construction diagram that describes the construction of a system by showing the system'southward:
- classes,
- their attributes,
- operations (or methods),
- and the relationships among objects.
Learn UML Faster, Better and Easier
Are yous looking for a Free UML tool for learning UML faster, easier and quicker? Visual Image Customs Edition is a UML software that supports all UML diagram types. It is an international award-winning UML modeler, and nonetheless it is easy-to-apply, intuitive & completely free.
Free Download
What is a Class?
A Grade is a design for an object. Objects and classes become mitt in paw. Nosotros can't talk about one without talking about the other. And the entire indicate of Object-Oriented Design is not about objects, information technology'southward well-nigh classes, because we use classes to create objects. And then a grade describes what an object volition be, simply it isn't the object itself.
In fact, classes describe the type of objects, while objects are usable instances of classes. Each Object was built from the aforementioned set of blueprints and therefore contains the same components (backdrop and methods). The standard meaning is that an object is an instance of a class and object - Objects accept states and behaviors.
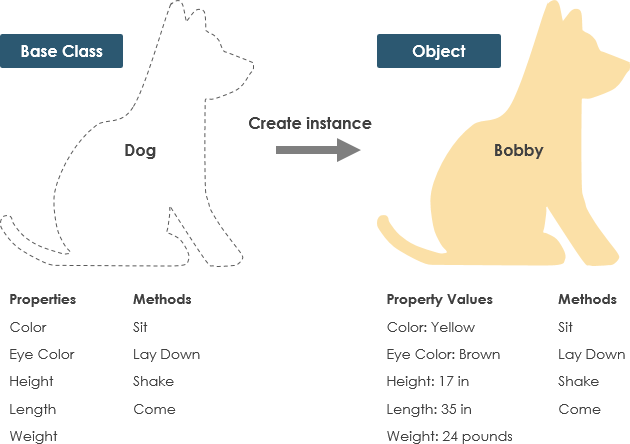
Example
A dog has states - colour, name, breed as well every bit behaviors -wagging, barking, eating. An object is an instance of a course.
UML Course Notation
A class stand for a concept which encapsulates land (attributes) and beliefs (operations). Each attribute has a type. Each operation has a signature. The class name is the only mandatory data .
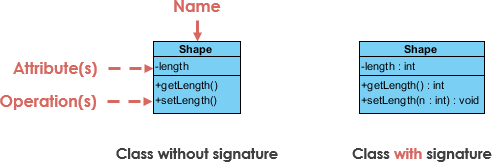
Class Name:
- The proper name of the grade appears in the offset sectionalization.
Class Attributes:
- Attributes are shown in the 2d partition.
- The attribute type is shown after the colon.
- Attributes map onto member variables (information members) in code.
Class Operations (Methods):
- Operations are shown in the tertiary partition. They are services the class provides.
- The render blazon of a method is shown afterward the colon at the cease of the method signature.
- The render type of method parameters are shown after the colon following the parameter proper name. Operations map onto class methods in lawmaking
Grade Visibility
The +, - and # symbols before an attribute and functioning name in a grade announce the visibility of the attribute and operation.
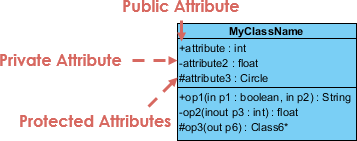
- + denotes public attributes or operations
- - denotes private attributes or operations
- # denotes protected attributes or operations
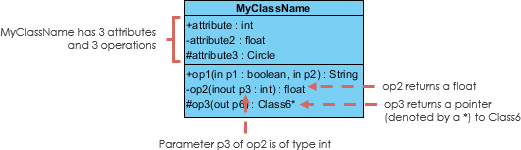
Parameter Directionality
Each parameter in an operation (method) may be denoted as in, out or inout which specifies its direction with respect to the caller. This directionality is shown before the parameter proper noun.
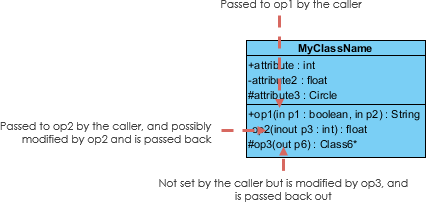
Perspectives of Course Diagram
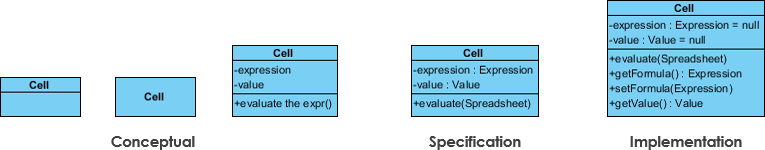
The option of perspective depends on how far along you are in the evolution process. During the conception of a domain model, for example, you lot would seldom move past the conceptual perspective. Analysis models will typically feature a mix of conceptual and specification perspectives. Design model development volition typically start with heavy emphasis on the specification perspective, and evolve into the implementation perspective.
A diagram can be interpreted from diverse perspectives:
- Conceptual: represents the concepts in the domain
- Specification: focus is on the interfaces of Abstract Data Type (ADTs) in the software
- Implementation: describes how classes volition implement their interfaces
The perspective affects the amount of detail to exist supplied and the kinds of relationships worth presenting. As we mentioned to a higher place, the class name is the only mandatory data.
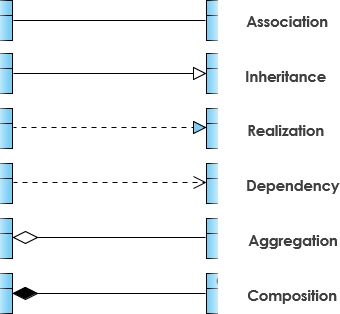
Relationships between classes
UML is not simply near pretty pictures. If used correctly, UML precisely conveys how code should be implemented from diagrams. If precisely interpreted, the implemented code will correctly reflect the intent of the designer. Tin yous describe what each of the relationships mean relative to your target programming language shown in the Figure below?
If you lot can't yet recognize them, no trouble this section is meant to assistance you to sympathize UML course relationships. A grade may be involved in one or more than relationships with other classes. A relationship tin can be 1 of the post-obit types:
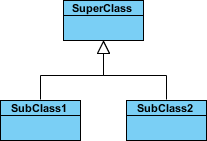
Inheritance (or Generalization):
A generalization is a taxonomic human relationship between a more general classifier and a more specific classifier. Each instance of the specific classifier is too an indirect example of the general classifier. Thus, the specific classifier inherits the features of the more general classifier.
- Represents an "is-a" relationship.
- An abstruse class name is shown in italics.
- SubClass1 and SubClass2 are specializations of SuperClass.
The figure below shows an example of inheritance hierarchy. SubClass1 and SubClass2 are derived from SuperClass. The relationship is displayed as a solid line with a hollow arrowhead that points from the child chemical element to the parent element.
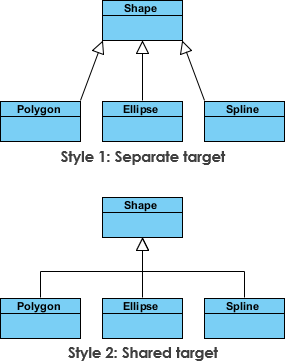
Inheritance Example - Shapes
The effigy below shows an inheritance example with 2 styles. Although the connectors are drawn differently, they are semantically equivalent.
Clan
Associations are relationships between classes in a UML Grade Diagram. They are represented by a solid line between classes. Associations are typically named using a verb or verb phrase which reflects the real earth problem domain.
Unproblematic Association
- A structural link between two peer classes.
- There is an association between Class1 and Class2
The figure below shows an example of unproblematic association. In that location is an clan that connects the <<control>> class Class1 and <<boundary>> class Class2. The human relationship is displayed as a solid line connecting the two classes.

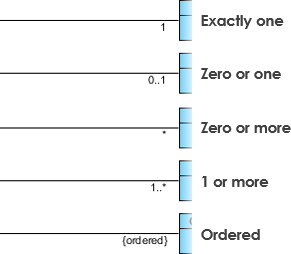
Cardinality
Cardinality is expressed in terms of:
- one to one
- i to many
- many to many
Assemblage
A special type of association.
- It represents a "part of" human relationship.
- Class2 is part of Class1.
- Many instances (denoted past the *) of Class2 tin can exist associated with Class1.
- Objects of Class1 and Class2 have separate lifetimes.
The effigy beneath shows an example of aggregation. The relationship is displayed as a solid line with a unfilled diamond at the association stop, which is connected to the grade that represents the aggregate.

Limerick
- A special type of aggregation where parts are destroyed when the whole is destroyed.
- Objects of Class2 alive and die with Class1.
- Class2 cannot stand past itself.
The figure below shows an example of composition. The human relationship is displayed as a solid line with a filled diamond at the association end, which is continued to the grade that represents the whole or composite.

Dependency
An object of one course might use an object of another class in the code of a method. If the object is not stored in any field, and then this is modeled every bit a dependency relationship.
- A special type of association.
- Exists between two classes if changes to the definition of one may cause changes to the other (just not the other way effectually).
- Class1 depends on Class2
The figure below shows an example of dependency. The relationship is displayed as a dashed line with an open arrow.
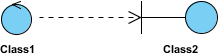
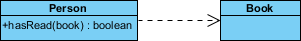
The effigy beneath shows another example of dependency. The Person class might have a hasRead method with a Book parameter that returns truthful if the person has read the volume (maybe past checking some database).
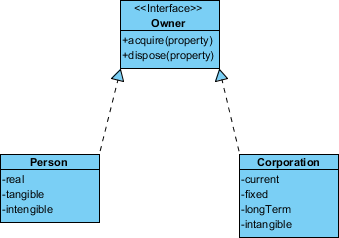
Realization
Realization is a relationship between the blueprint class and the object containing its respective implementation level details. This object is said to realize the blueprint grade. In other words, you tin understand this as the relationship betwixt the interface and the implementing class.
For example, the Owner interface might specify methods for acquiring property and disposing of holding. The Person and Corporation classes need to implement these methods, perhaps in very dissimilar ways.
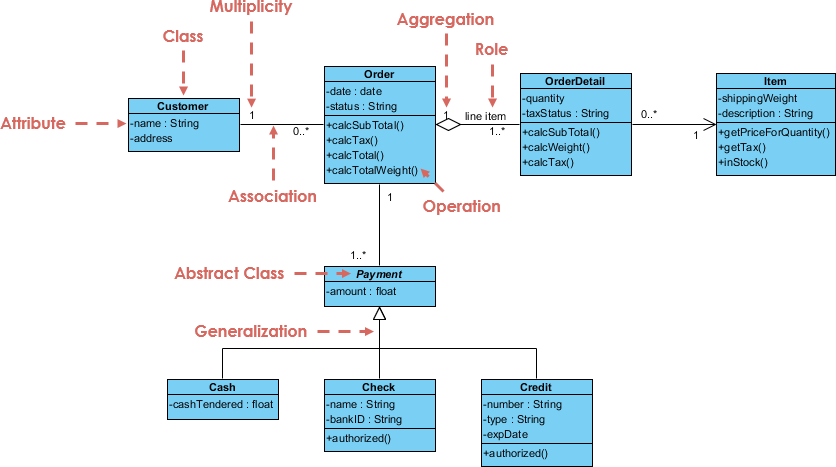
Course Diagram Example: Society System
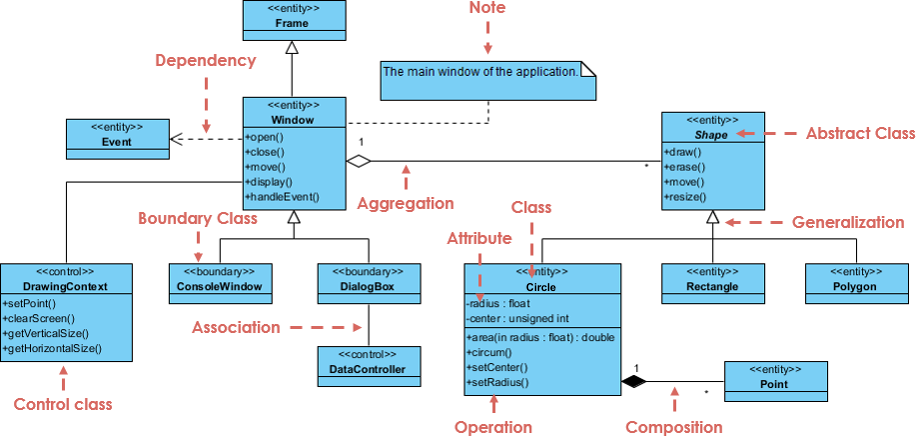
Class Diagram Case: GUI
A form diagram may also have notes fastened to classes or relationships.
Try to Describe UML Class Diagram Now
You lot've learned what a Class Diagram is and how to draw a Grade Diagram. Information technology'due south time to draw a Course Diagram of your own. Get Visual Epitome Community Edition, a complimentary UML software, and create your own Class Diagram with the costless Class Diagram tool. It's easy-to-use and intuitive.
Free Download
Source: https://www.visual-paradigm.com/guide/uml-unified-modeling-language/uml-class-diagram-tutorial/
Post a Comment for "How to Draw Class Diagram in Visual Paradigm"